Pop culture would have you believe that eating a bag of weed will leave you stoned out of your gourd, but it's not that simple. The reason? Decarboxylation — or rather, a lack thereof. Learn how decarboxylation works, why it's important, and tips for consumers with both high and low tolerances.
What is decarboxylation?
Decarboxylation — or "decarbing" — is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group (COOH) from a molecule. This process often occurs when heating organic compounds like cannabinoids, amino acids, or carboxylic acids.
In the context of cannabis, decarboxylation is a critical step to activate the psychoactive properties of the cannabinoids present in the plant, like THC and CBD. Raw cannabis plants contain THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and CBDA (cannabidiolic acid), which are the non-psychoactive precursors of THC and CBD. When you heat cannabis flower through smoking, vaporizing, or cooking, you remove a carboxyl group from THCA and CBDA, converting them into their activated chemical forms, THC and CBD. The same goes for other cannabinoid acids.
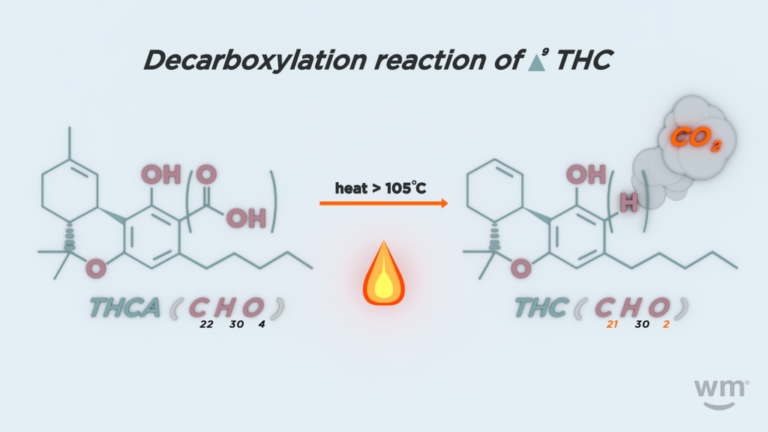 Photo by: Weedmaps
Photo by: WeedmapsImage lightbox

These activated chemical forms are capable of interacting with your endocannabinoid system. It's the decarboxylation process that delivers the high or therapeutic relief many cannabis consumers seek.
How decarboxylation works
Decarboxylation is the process of applying heat to cannabis flower to activate the psychoactive properties of cannabinoids in that flower. It works in various ways:
- Heat application: Raw or cured flowers from the cannabis plant contain non-psychoactive cannabinoid acids like THCA and CBDA. While these compounds may have some potential therapeutic properties, they will not get you high. To feel the psychoactive effects of cannabis, you need to apply heat to detach the carboxyl group (COOH) from the molecules and convert these acids into their active forms of THC and CBD.
- Temperature and time: Decarboxylation requires specific temperatures and durations for optimal results. Generally, you expose cannabis to temperatures between 200 - 290°F (104 - 118°C). The process can take between 7 - 60 minutes depending on the temperature. Lower temperatures require more time, while higher temperatures speed up the process.
- CO2 release: As the carboxyl group detaches, it releases carbon dioxide (CO2) as a byproduct. During the release of CO2, the cannabinoids in the plant matter are converted into their active forms. Once the process is complete, your flower will have a higher concentration of active THC and CBD, making it more potent and effective for homemade infusions, edibles, tinctures, or topicals.
Do you need to decarb weed to make edibles?
Yes, if you want to achieve a psychoactive or intoxicating high, then you need to decarb your weed before making edibles. If you don't decarb your cannabis before use, the resulting infusions you make will be far less potent and may not produce the effects you were hoping for. But if you're completely new to cannabis, have a very low tolerance for THC, or want to try a cannabis product without experiencing that classic weed high, then you may want to skip the decarboxylation step entirely.
How to decarb weed
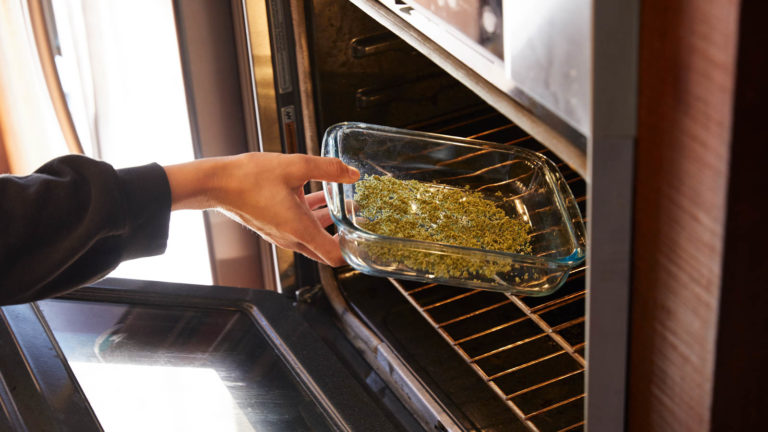 Photo by: Gina Coleman/Weedmaps
Photo by: Gina Coleman/WeedmapsImage lightbox

Materials
- Eighth of cannabis flower
- Oven
- Grinder or scissors
- Baking sheet
- Parchment paper
- Oven mitts
- Spatula or spoon
- Airtight container
Instructions
Follow these steps to decarb weed in the oven before making edibles, tinctures, or cannabis-infused oils:
Step 1: Preheat oven
Set your oven to 250°F (121°C) and allow it to preheat. The temperature is crucial to ensure proper decarboxylation without destroying the cannabinoids and terpenes.
Step 2: Prepare cannabis
Break up your buds into small, pea-sized pieces using your hands or a grinder. Don't grind it too fine, as this can lead to uneven decarboxylation and makes it harder to strain.
Step 3: Line baking sheet
Use a baking sheet with raised edges to prevent any spillage or loss of material. Line the sheet with parchment paper to keep your weed from sticking and ensure easy cleanup.
Step 4: Spread cannabis
Spread the ground cannabis evenly across the parchment paper on the baking sheet. The layer should be thin and without clumps for even heating.
Step 5: Bake
Place the baking sheet with cannabis in your preheated oven for about 20 minutes. The time may vary depending on the freshness and moisture content of your cannabis. If it's particularly moist, you may need to extend the baking time. Keep an eye on the color; the flower should turn from a bright green to a golden brown.
Step 6: Monitor and stir
Check on the cannabis halfway through the baking process — about 10 minutes. If it's already golden brown and dry, take it out. Give it a gentle stir to ensure even decarboxylation.
Step 7: Remove sheet from oven
After 20 minutes, the cannabis should be golden brown. Carefully remove the baking sheet from the oven.
Step 8: Cool
Allow the flower to cool completely on the baking sheet. It will be quite fragile and crumbly at this point, so handle it gently to avoid losing any material.
Step 9: Store or use
Once the decarboxylated cannabis is cool, you can pulse it in a food processor to add it directly to food or grind it into a fine powder for beverages. You can also use your decarboxylated herb to make potent cannabutter the traditional way or via a slow cooker for homemade cannabis edibles. Otherwise, store your decarbed weed in an airtight container away from direct sunlight and heat.
Decarboxylation temperature chart
Decarbing weed is a function of heat and time. The following chart shows the recommended temperatures and times for activating THCA, CBDA, and CBGA, according to Dr. Adie Rae, neuroscientist and scientific adviser to Weedmaps. The highlighted sections indicate Dr. Rae's recommendations for the ideal temperature and time for a balanced conversion.
Regardless of the cannabinoid, Dr. Rae suggests decarbing weed at 250°F (120°C) for 20 minutes.
How to use decarbed weed
Once you have decarboxylated weed, you can use it in a number of ways:
- Infuse it into oil or butter: You can infuse decarboxylated weed into oil or butter, which you can then use in cooking or baking. This is a popular starting point for homemade cannabis edibles.
- Make tinctures: Tinctures are alcohol-based cannabis extracts that can be added to drinks or used sublingually (under the tongue). Soak decarboxylated weed in high-proof alcohol for several weeks for a simple tincture or learn more about the process in our guide to making weed tinctures.
- Make topicals: Infuse decarboxylated weed into oils or creams to make cannabis topicals, which you can apply to your skin for potential localized relief.
- Make capsules: You can put decarbed weed directly into capsules for easy dosing. Making your own weed capsules is a convenient method for people who do not want to smoke or eat cannabis.
When using decarboxylated weed, start with a small amount and wait to see how it affects you before consuming more. Start low and go slow, the effects of decarboxylated weed can be more potent and longer-lasting than raw or cured cannabis.
Key tips and takeaways
There are a few main takeaways to consider when it comes to decarbing weed:
- Don't decarboxylate if you don't want to get high. Cannabis decarboxylation is necessary for consumers who want to achieve maximum potency and reap the potential therapeutic and psychoactive effects of THC and CBD. If you intend to add cannabis directly to food or drink to achieve a potent high, the above steps will help you activate the cannabinoids to get the most out of your cannabis. However, low-dose consumers or those who are new to cannabis can still reap some of the potential benefits and avoid a potent psychoactive high by skipping the decarbing step.
- Don't decarb weed before smoking. You don't need to decarb weed before vaping or smoking since the heat involved in either process will convert the cannabinoid acids to cannabinoids.
- Get the temperature right. The right temperature will activate as much of the flower's cannabinoid content as possible without destroying too many terpenes and ruining the smell, taste, and possible entourage effects. Decarbing weed at a high temperature — hotter than 300°F (148.9°C) — may cause degradation. Terpenes may evaporate, and the smell and flavor may be unsavory.
- Invest in an accurate oven thermometer. To ensure that you are decarbing weed at the right temperature, use an accurate oven thermometer to monitor the temperature in your oven.
- Grind weed before decarbing. Grinding your weed to a rough but not too fine texture before decarbing will increase the surface area and help ensure that all parts are exposed to heat. This can help improve the efficiency of the decarboxylation process.
FAQ
What is the purpose of decarbing weed?
Decarbing weed converts the non-psychoactive THCA in cannabis into psychoactive THC, making the cannabis more potent for use in edibles, tinctures, and other non-smoking consumption methods.
What temperature should I use to decarb weed?
The recommended temperature for decarbing weed is 250°F, or 115°C. This temperature allows for effective decarboxylation without destroying cannabinoids and terpenes.
How long does it take to decarb weed?
Decarbing weed typically takes around 20 minutes in the oven. However, the time may vary depending on factors like the starting freshness and moisture content of the cannabis. The final color of your decarbed weed should be a light golden brown.
Can I decarb weed in a microwave or on a stovetop?
Though you can, it's not recommended to decarb weed in a microwave or on a stovetop, as these methods can lead to uneven heating and may destroy cannabinoids and terpenes in the process. An oven provides the most consistent and controlled heating environment for decarboxylation.
Can I decarb weed using a sous vide method?
Yes, sous vide is an alternative method for decarbing weed that involves sealing the cannabis in a vacuum-sealed bag and immersing it in a temperature-controlled water bath. This method allows for precise temperature control and even heating, reducing the risk of burning or losing cannabinoids and terpenes. To decarb weed using sous vide, set the water bath temperature to 250°F and keep the sealed weed submerged for 60 - 90 minutes.
Won't the weed decarb on its own during the cannabutter infusion process?
You might wonder why you can't just skip a step and decarboxylate weed while infusing it in butter. Dr. Rae explained, “That usually requires a precise cooking device — like a sous vide water bath — to hold the temperature exactly where you want it for exactly how long you want to." If you want to go the sous vide route and have the proper tools at your disposal, have at it. Otherwise, it's likely easiest for most home cooks to decarboxylate their weed and then infuse it into butter or coconut oil.
Do you need to decarb weed before smoking it?
Smoking or vaporizing cannabis will automatically decarb any THC present, but for other uses like making edibles, the decarb step is crucial to achieving a potent head high.
What's the difference between drying, curing, and decarbing weed?
The drying and curing processes happen after the plant has been harvested in order to help rid the weed of moisture. While minuscule amounts of cannabinoid acids are converted during these processes, it's not enough to deliver the effects that recreational and medicinal consumers typically seek.
Does decarboxylation destroy CBD?
No, when performed correctly, decarboxylation does not ruin CBD. Decarboxylation is actually necessary to activate CBD. As with THC, the raw cannabis plant does not contain CBD molecules. Instead, it contains cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), which does not interact with your body the same way CBD does.
To convert that CBDA into CBD, and enjoy its potentially therapeutic effects, decarboxylate your weed.
What happens if you decarb weed for too long?
Over-decarboxylation can cause the following issues:
- Loss of potency: Extended exposure to heat can break down THC into CBN (cannabinol), a less psychoactive compound. This results in a less potent product with potentially different effects, such as increased sedation and drowsiness.
- Degradation of terpenes: Terpenes are the aromatic compounds responsible for the unique flavors and scents of cannabis strains. Excessive heat and extended decarboxylation times can cause the terpenes to evaporate or degrade, resulting in a less flavorful and aromatic product.
- Loss of other cannabinoids: Prolonged decarboxylation can also degrade other cannabinoids like CBD, which play a crucial role in the overall effects and medicinal benefits of the plant.
To avoid over-decarboxylation, carefully monitor the temperature and time during the process. Use an oven thermometer for accurate temperature readings and check on the cannabis regularly, looking for a color change from bright green to golden brown.
What's the difference between decarb temps and boiling temps?
Knowing the boiling point of a particular cannabinoid or terpene is only useful for vaping flower and only if you have a vaping device capable of achieving precise temperatures. You could, for example, customize your session to deliver the maximum potency for whichever terpene or cannabinoid you choose by knowing the boiling temperature of that compound.




